Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-03 Origin: Site








The aging population in the United States demands specialized furniture solutions that balance comfort, safety, regulatory compliance, and durability. As a project contractor, interior designer, or facilities manager, selecting the right chairs for the elderly US market requires understanding specific design standards, procurement criteria, and vendor selection processes. This comprehensive guide provides B2B professionals with essential specifications, compliance requirements, and strategic considerations for successfully sourcing elderly care seating across assisted living facilities, skilled nursing homes, senior living communities, and medical care environments.

The US senior care furniture market continues to experience robust growth, driven by demographic trends and increased emphasis on resident quality of life. Facilities investing in proper elderly seating solutions see measurable improvements in resident satisfaction, reduced fall incidents, and lower staff injury rates—making informed procurement decisions essential for both compliance and operational excellence.
The global ergonomic furniture market reached $11.13 billion in 2025 and is projected to expand to $19.12 billion by 2033, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.98%. The senior living segment captures a significant and growing portion of this market, with nursing home and assisted living facilities serving as primary drivers.
The United States maintains the highest concentration of specialized elderly care furniture demand, with over 4.7 million seniors currently residing in care facilities, according to recent industry data. This population is projected to increase 35% by 2030, creating substantial procurement demand for compliant, durable seating solutions.
FF&E (Furniture, Fixtures, and Equipment) procurement for senior living facilities involves specialized vendors, group purchasing organizations (GPOs), and direct manufacturers. Key procurement stakeholders include:
Facility Operators: Assisted living, skilled nursing, memory care, and continuing care retirement communities
Design Professionals: Interior designers and architects specializing in senior living projects
Project Contractors: General contractors managing facility renovations and new construction
Healthcare Administrators: Directors of operations managing facility furnishings
Group Purchasing Organizations: Providing aggregate purchasing power and vendor relationships
Understanding this B2B ecosystem is essential for specifying appropriate seating solutions that meet budget constraints, timeline requirements, and compliance standards.

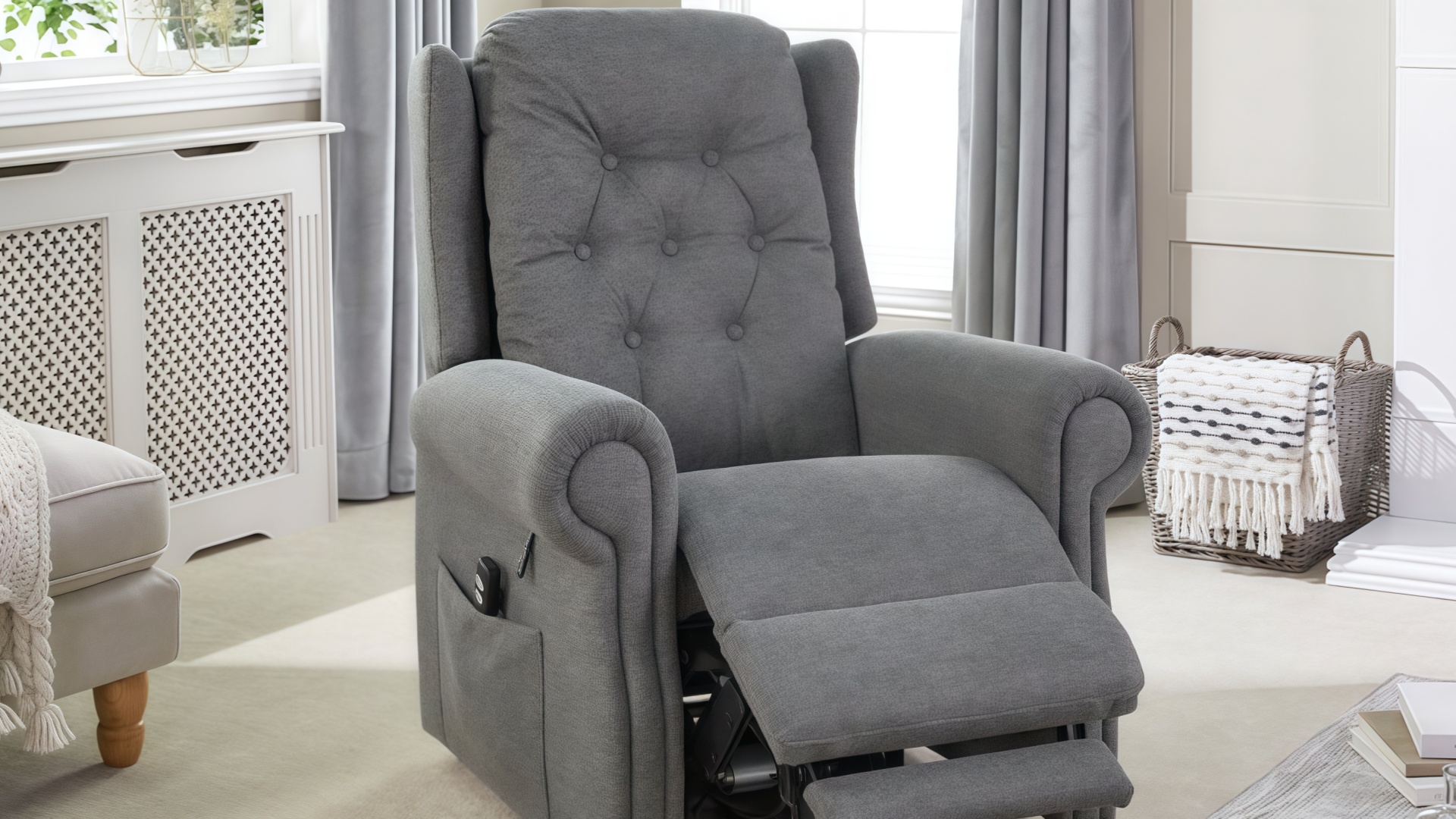
Optimal seat height represents the most critical specification for elderly seating in the US market. Current evidence-based guidelines recommend:
Standard seat height: 17-20 inches (432-508 mm) from floor to finished seat surface
For optimal transfer assistance: 18-19 inches is ideal for 95% of elderly users
High-risk populations: Facilities should maintain variety, ranging from 16-22 inches to accommodate diverse resident body types
Research from aged care specialists indicates that chairs with seat heights below 17 inches significantly increase fall risk during standing transfers, while heights exceeding 22 inches create awkward knee angles and discomfort for typical elderly residents.
Backrest dimensions are equally critical:
Minimum backrest height: 15 inches above seat surface
Lumbar support placement: 4-6 inches above seat surface
Overall chair height: 30-36 inches total, depending on seat height and backrest design
Proper seat dimensions prevent pressure points and maintain circulation during extended sitting periods:
Seat depth: 380-440 mm (15-17.5 inches) allows full thigh support without forcing slouching
Seat width: 16-20 inches accommodates average elderly residents; 20-24 inches for bariatric applications
Knee clearance: Minimum 6 inches behind knees prevents circulation restriction
Seats exceeding 18 inches in depth create problems for shorter residents (below average height), forcing them to slouch forward to contact the backrest, reducing spinal support and comfort.
Footrest height should be calibrated to specific seat heights:
Formula: Seat height minus 8 inches = ideal footrest height
Example: 18-inch seat = 10-inch footrest height
Footrest platform size: Minimum 4-6 inches wide for stable foot placement
Armrest specifications:
Height: 7-10 inches above seat surface (accounting for upholstery compression)
Depth into seat width: 2-4 inches from seat edge
Structural requirement: Must support 300+ pounds during transfer assistance
Padding: Minimum 1.5 inches of high-density foam, minimum R-value 25
Single-armrest or asymmetrical armrest designs facilitate easier seating and standing for residents with unilateral weakness or hemiplegic conditions.

High-traffic elderly care environments require performance-grade upholstery meeting specific durability and maintenance criteria:
Performance Fabric Requirements:
Wyzenbeek abrasion rating: Minimum 50,000 cycles (preferably 100,000+)
Pilling resistance: Grade 4-5 rating (industry standard ASTM D3945)
Stain resistance: Class A or equivalent (AATCC rating 8 or above)
Seam strength: Minimum 25 pounds per linear inch
Fabric Types for Elderly Care Settings:
| Fabric Type | Durability | Cleanability | Comfort | Best Use |
Vinyl/PVC | ✓✓✓ Excellent | ✓✓✓ Excellent | ✓ Fair | High-traffic, medical settings |
Leather/Polyurethane | ✓✓✓ Excellent | ✓✓ Good | ✓✓ Good | Premium assisted living |
Performance Microfiber | ✓✓✓ Excellent | ✓✓ Good | ✓✓ Good | Balanced facilities |
Solution-Dyed Acrylic | ✓✓ Good | ✓✓ Good | ✓✓✓ Excellent | Comfort-priority facilities |
Polyester Blend | ✓ Fair | ✓ Fair | ✓✓✓ Good | Budget-constrained projects |
Color and Pattern Selection: Darker colors and subtle patterns are recommended in high-traffic settings; however, color variety can support wayfinding and environmental psychology in memory care and dementia-focused units.
Frame material requirements:
Solid wood: Hardwoods (oak, maple) with mortise-and-tenon joinery preferred; softwoods acceptable with reinforcement
Metal frames: Welded steel or aluminum tubing, minimum wall thickness 0.095 inches
Engineered wood: Acceptable if laminated with hardwood veneers; particleboard not recommended for high-wear applications
Structural load requirements:
Standard elderly seating: Minimum 300-pound weight capacity
Bariatric furniture: 400-600+ pound capacity (specifically engineered models)
Testing standard: Furniture should comply with ANSI/BIFMA safety standards
All elderly care seating specified for US facilities must comply with multiple regulatory frameworks:
Flammability Standards:
CAL TB 117 (California Title 24): All upholstered furniture must meet strict flammability standards; TB 117-2013 revised standards eliminated certain flame retardant chemicals
NFPA 260: Standard for flame testing of materials used in interior construction
Federal regulations: All furniture sold in the US must pass 16 CFR 1633 cigarette ignition test
Accessibility Standards:
ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act): Seating must accommodate users of varying body dimensions and mobility abilities
Approach space: Minimum 36-inch width for wheelchair or mobility device access
Armrest height and placement: Must permit safe side transfers for people with mobility limitations
ANSI/BIFMA Certification: The standard for commercial furniture safety and performance
M7.1: General office furniture
X5.4: Seating comfort and ergonomics
Certification ensures third-party testing of structural integrity and load capacity
GREENGUARD Gold Certification: Increasingly required by facilities emphasizing indoor air quality
Restricts off-gassing of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
Important for residents with respiratory sensitivities
SOFA Certification (when applicable): Industry standards for upholstered furniture in high-traffic settings
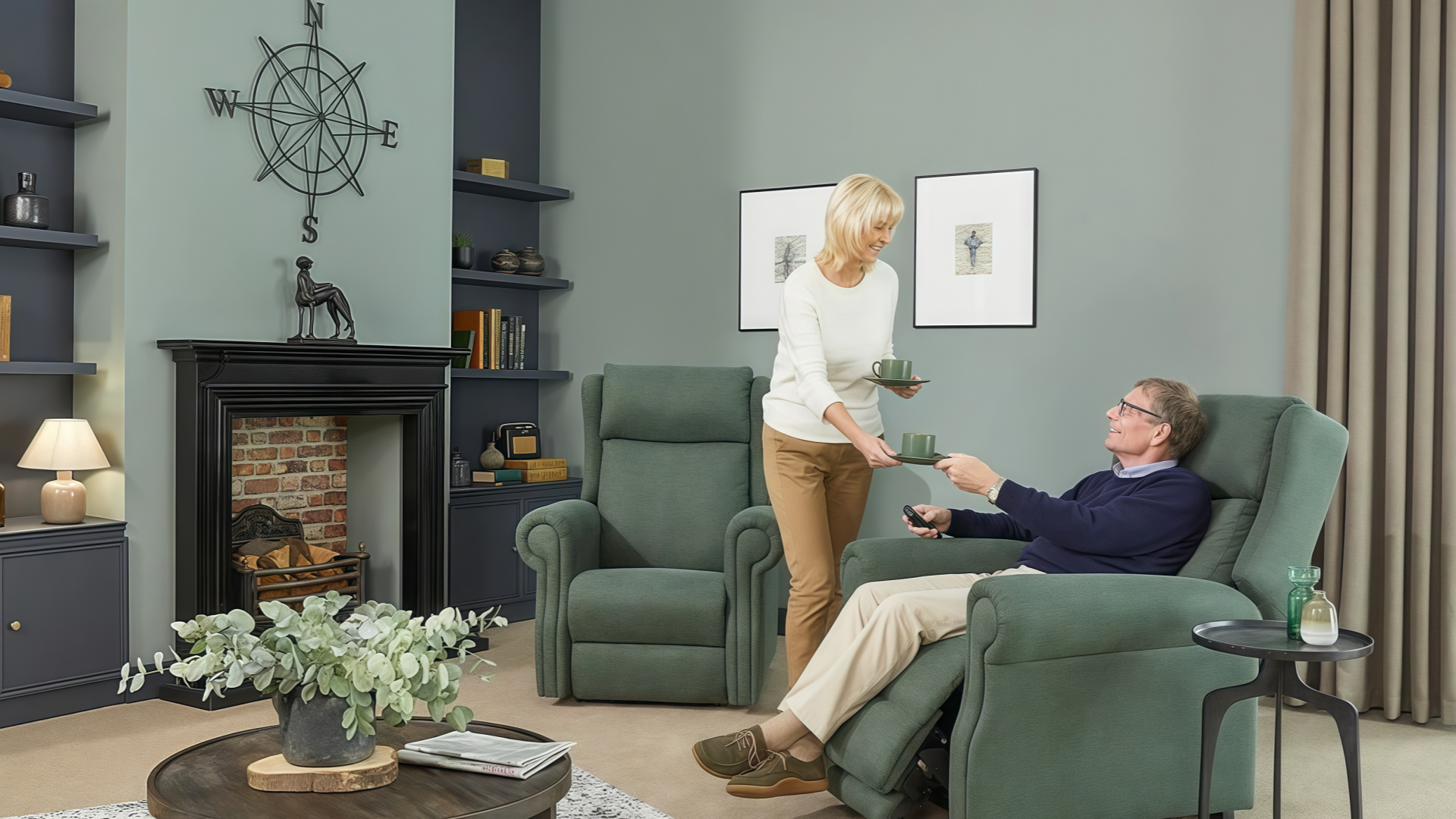
Specifications:
Seat height: 18-19 inches
Seat width: 18-20 inches
Seat depth: 16-18 inches
Backrest height: 15-18 inches above seat
Armrest: Yes (structural transfer support)
Footrest: Yes (integrated or separate)
Applications: Common areas, activity rooms, television lounges, dining areas with optional arm support seating
Best Practice: Specify 30-40% with high-back (18"+) for additional lumbar and cervical support
Budget Allocation: $500-$1,200 per chair (standard specifications)

Specifications:
Seat height: 18-20 inches (adjustable models available)
Medical-grade fabrics: Antimicrobial or easily sanitizable
Pressure-relief cushioning: High-density foam (HR foam, minimum 1.8 lb/cubic foot density)
Structural feature: Removable seat cushion for cleaning/replacement
Footrest: Integral design with non-slip surface
Armrest: Padded, washable covers preferred
Applications: Rehabilitation units, bariatric care, post-acute care facilities, hospice care
Specialized Features:
Some models include memory foam or gel-infused cushioning for extended pressure relief
Recline functions preferred for patients with limited mobility
Antimicrobial upholstery addressing healthcare-acquired infection (HAI) prevention
Budget Allocation: $1,200-$2,500 per chair
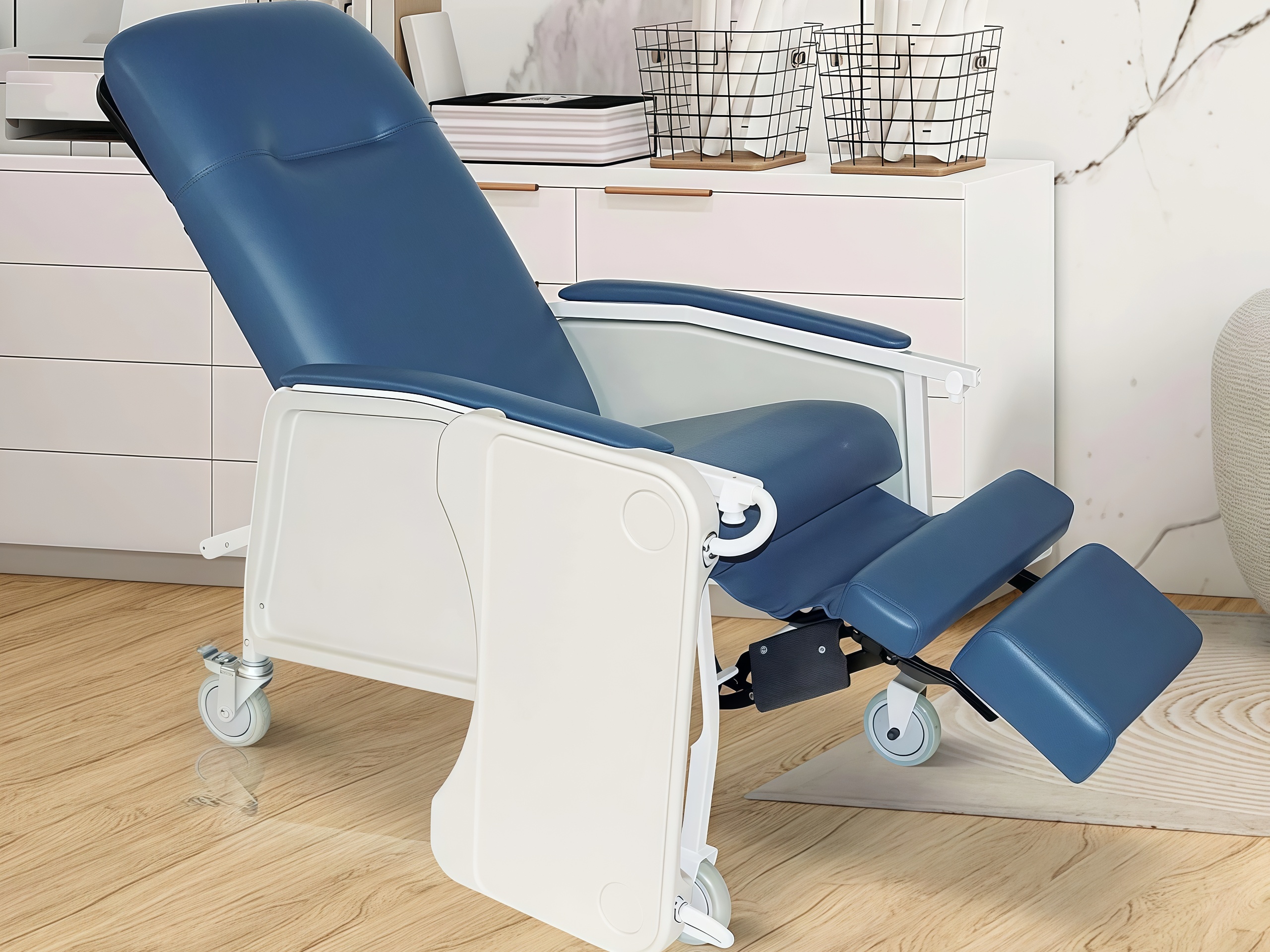
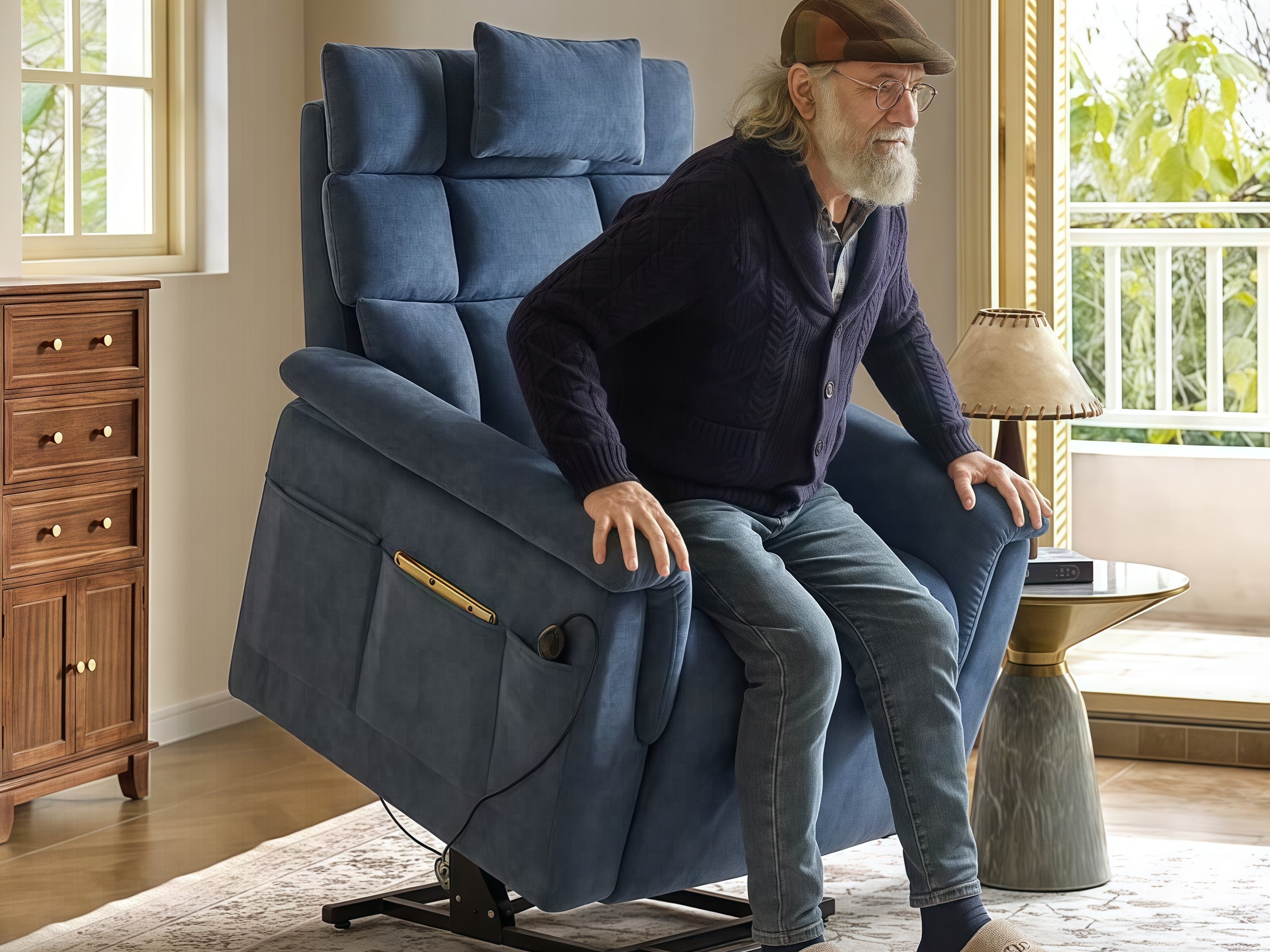
Specifications:
Seat height: Variable (16-22 inches, electronically adjustable)
Lift mechanism: Electric, assists user from seated to standing position
Control system: Wired or wireless remote, simple one-button operation
Weight capacity: 350+ pounds (standard); 600+ pounds (bariatric models)
Safety feature: Automatic hold-down preventing lift during occupied conditions except during controlled standing sequence
Footrest: Integral, automatically positions during lift cycle
Applications: High-dependency care units, skilled nursing facilities, dementia care (supervised settings only)
Regulatory note: Staff training mandatory; requires supervision for most users
Budget Allocation: $2,500-$5,000+ per chair

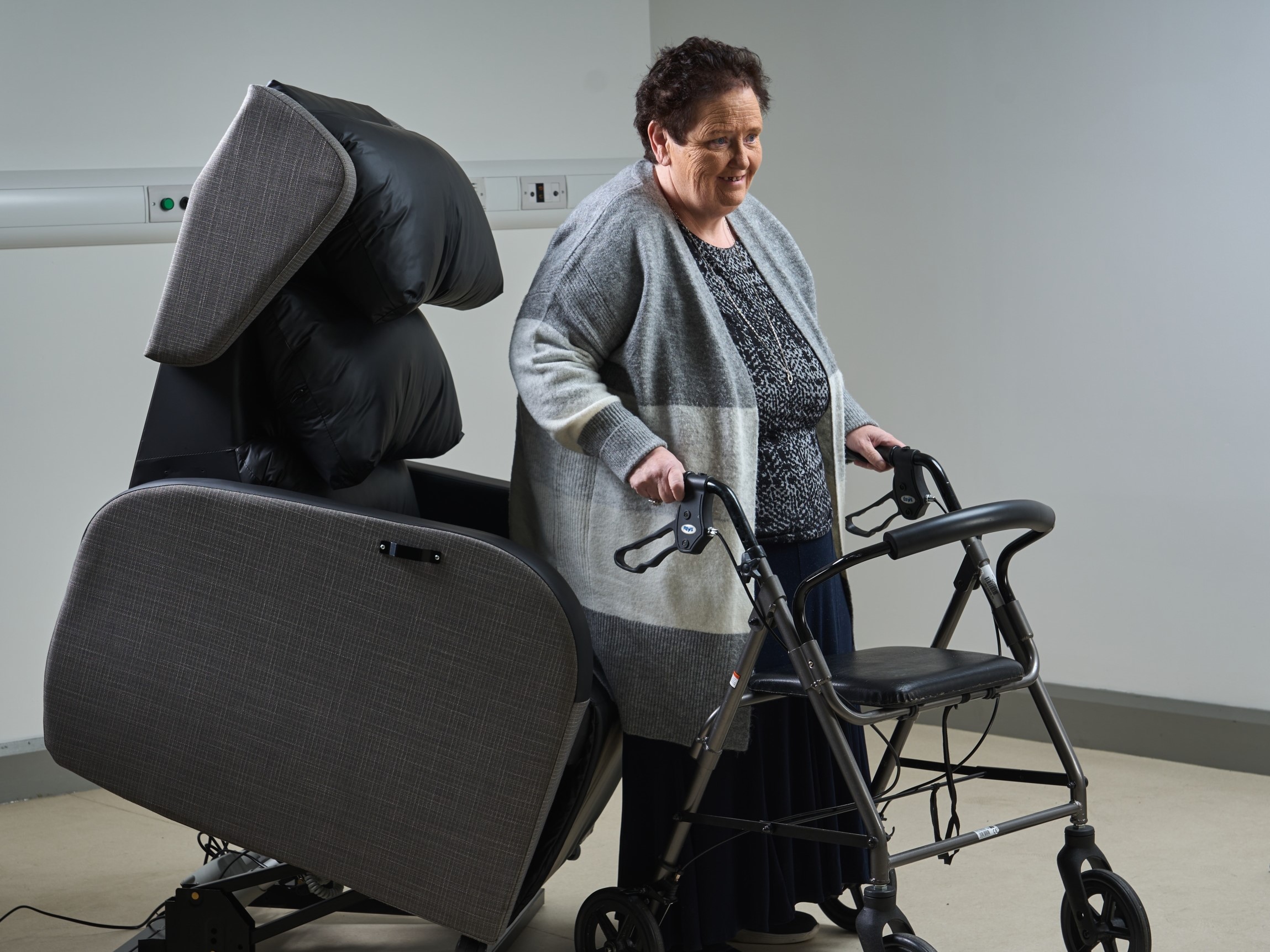
Specifications:
Seat width: 22-30 inches
Seat height: 18-20 inches (extended depth frames support higher weight)
Weight capacity: 400-600+ pounds
Reinforced frame: Heavy-gauge steel or engineered wood reinforcement
Double-stitched seams: Higher load-bearing requirement
Extended armrest strength: Must support bariatric user transfers
Applications: Facilities with 10-15% bariatric population projections
Procurement consideration: Specify integrated bariatric seating throughout facility rather than segregating; addresses dignity and inclusion
Budget Allocation: $1,500-$3,000 per chair

When evaluating manufacturers and distributors for elderly care seating:
Essential Criteria:
1. Compliance Documentation: Verify CAL TB 117-2013, BIFMA, and ADA certifications
2. Warranty Structure: Minimum 5-year frame warranty; 3-year upholstery coverage
3. Lead Times: Critical for phased renovations; confirm manufacturing and delivery capacity
4. Customization Capability: Design flexibility for specific facility layouts and color schemes
5. Local Service Support: Repair and maintenance availability within region
Financial Considerations:
Negotiate volume pricing for large facility projects (typically 20-30% discounts for 50+ units)
Evaluate total cost of ownership, not just acquisition cost
Consider maintenance and replacement cycle costs (fabric refresh every 5-7 years typical)
Group Purchasing Organization (GPO) participation offers 15-25% savings for qualified facilities
Professional elderly care facilities increasingly prioritize "hospitality design"—creating homelike environments rather than institutional appearance.
Design considerations:
Color coordination: Specify complementary upholstery colors coordinating with wall finishes and carpet
Style consistency: Select seating styles coordinating with overall interior design theme
Accessibility integration: Ensure seating doesn't create visual wayfinding confusion
Dementia-friendly design: High-contrast colors assist residents with visual processing challenges
Contemporary designers recommend 60% neutral foundation colors (grays, taupes, warm whites) with 30% accent colors and 10% bold/feature colors in seating specifications.
| Specification Category | Standard Requirement | Professional Best Practice |
Seat Height | 17-20 inches | 18-19 inches (optimal for 95% elderly) |
Backrest Height | Minimum 15" above seat | 16-18 inches (cervical support) |
Armrest Load Capacity | 300+ pounds minimum | 350+ pounds (transfer safety margin) |
Fabric Durability | Wyzenbeek 50,000 cycles | 100,000+ cycles (7-10 year lifespan) |
Weight Capacity | 300-350 pounds standard | 400+ pounds (25% safety margin) |
Cushioning | High-density foam | HR foam 1.8+ lb/ft³, pressure relief |
Compliance | CAL TB 117-2013 | BIFMA + GREENGUARD certification |
Warranty | 3-5 years typical | 5-7 year protection (optimal) |
Typical facility composition and associated costs:
| Category | Percentage of Inventory | Unit Cost Range | Total Per Facility (100 chairs) |
Standard Activity/Lounge | 50% | $500-$1,200 | $25,000-$60,000 |
Medical Grade Care | 25% | $1,200-$2,500 | $30,000-$62,500 |
Lift/Power-Assist | 15% | $2,500-$5,000 | $37,500-$75,000 |
Bariatric Specialty | 10% | $1,500-$3,000 | $15,000-$30,000 |
TOTAL PROJECT COST | 100% | — | $107,500-$227,500 |
Cost management strategies:
GPO purchasing: 15-25% savings through group purchasing organizations
Phased procurement: Spread purchases across fiscal years to manage budget impact
Refurbishment programs: Selected units refresh/reupholster rather than full replacement (40-50% cost savings)
Negotiated volume pricing: Direct manufacturer quotes often 20-30% below list pricing for facilities
Typical 12-month project timeline:
| Phase | Timeline | Key Activities |
Planning | Months 1-2 | Needs assessment, budget approval, vendor RFP |
Specification Development | Months 2-3 | Design standards, compliance documentation, selection |
Procurement | Months 3-5 | Vendor negotiations, contracts, lead-time confirmation |
Manufacturing | Months 5-10 | Custom fabrication (8-12 weeks typical) |
Delivery/Installation | Months 10-12 | Phased delivery, acceptance, staff training |
Post-Installation | Months 12+ | Warranty activation, maintenance protocol establishment |
Successful procurement of chairs for the elderly US market requires integration of ergonomic science, regulatory compliance, design aesthetics, and B2B vendor relationships. By leveraging the specifications, standards, and procurement strategies outlined in this guide, project contractors, interior designers, and facilities managers can confidently specify elderly care seating solutions that enhance resident quality of life, ensure regulatory compliance, reduce fall risk, and deliver long-term value.
The investment in properly specified elderly care seating directly correlates with improved resident outcomes, reduced staff injuries, and enhanced facility reputation—making informed procurement decisions a cornerstone of professional senior living facility development and management.
Key Takeaway: Partner with qualified vendors, prioritize compliance documentation, specify for durability and comfort, and design for the diverse needs of elderly residents to ensure optimal results in elderly care seating projects.